Top Inspection Strategies Using G5020 Metal Detectors
- Top Inspection Strategies Using G5020 Metal Detectors
- Why choose a metal detector for food industry inspection — overview and priority goals
- Product snapshot: Food Metal Detector Manufacturer For Reject Defective Products G5020
- Understand the detection environment: product effect, packaging, and frequency setup
- Installation and line integration — optimizing for a metal detector for food industry lines
- Calibration and sensitivity testing — practical steps for reproducible results
- Validation and verification — meeting regulatory requirements with a metal detector for food industry
- Reject strategies: minimize product loss while ensuring safety
- Hygiene and maintenance — essential for a certified metal detector for food industry
- Troubleshooting common issues with metal detector for food industry lines
- Data logging and traceability — turning detector events into actionable insights
- How the G5020 compares: multi-frequency vs single-frequency metal detector performance
- Operational SOP checklist for using a metal detector for food industry inspection
- Brand advantages: Why choose the Food Metal Detector Manufacturer For Reject Defective Products G5020
- Case example: reducing false rejects in a mixed‑product snack line
- FAQs — common questions about using the G5020 metal detector for food industry applications
- Contact and next steps — view the product or speak with an expert
- Sources
- Contact / View product
Top Inspection Strategies Using G5020 Metal Detectors
Why choose a metal detector for food industry inspection — overview and priority goals
Food manufacturers must balance product safety, regulatory compliance, minimal product loss, and continuous production throughput. A metal detector for food industry use must therefore deliver consistent sensitivity to a range of metal types (ferrous, non‑ferrous, stainless), be hygienic, and integrate smoothly into production lines — especially where multihead weighers and automated reject systems are used. The Food Metal Detector Manufacturer For Reject Defective Products G5020 addresses these priorities with multi‑frequency detection, a hygienic conveyor design, and easy disassembly for maintenance.
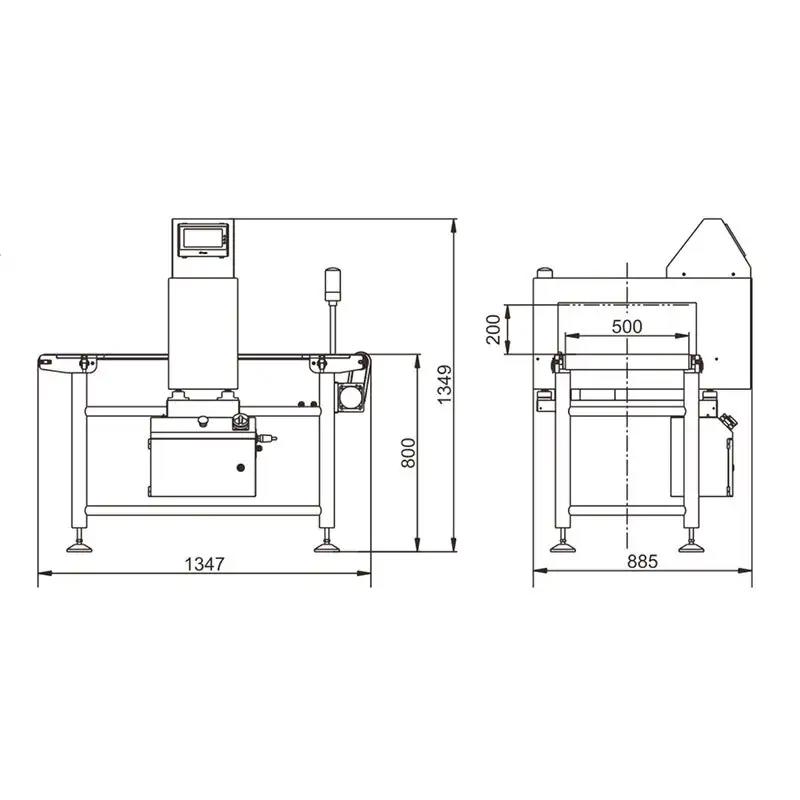
Product snapshot: Food Metal Detector Manufacturer For Reject Defective Products G5020
The G5020 multi-frequency metal detector features a specialized conveyor belt designed to reduce contamination risks, ensure smooth operation, and maintain high detection sensitivity. It is easy to disassemble for convenient maintenance. Ideal for detecting metal contaminants in food, pharmaceuticals, spices, plastics, electronics, textiles, toys, handicrafts, and more.
Understand the detection environment: product effect, packaging, and frequency setup
Setting up a metal detector for food industry operations begins with profiling the products you inspect. “Product effect” refers to how the product’s conductivity and density can mask metal signals. High‑moisture, high‑salt, or dense products (e.g., wet sausages, cheeses, sauces) generate stronger background signals and require different detector tuning than dry products like chips or cereals.
Best practice is to group products with similar composition and run separate detector recipes. The G5020's multi‑frequency capability lets you select or combine frequencies to reduce product effect and improve detection of specific metals (e.g., low‑magnetic stainless steel). Lower frequencies are better for detecting stainless steel and non‑ferrous metals in wet products; higher frequencies can be more sensitive to small ferrous particles in dry products. Always validate sensitivity for each product/packaging combination (see validation section).
Installation and line integration — optimizing for a metal detector for food industry lines
Correct physical installation prevents common performance issues. Position the G5020 on a level frame, clear of electromagnetic interference sources (motors, large variable speed drives) and away from vibration. Maintain straight, supported product flow into and out of the aperture — turbulence or product tumbling can reduce sensitivity and increase false rejects. If integrating with a multihead weigher, align the discharge path so the detector sees the product in a stable, repeatable orientation.
For automated reject systems: ensure reject timing is synchronized to belt speed and product length so the rejected item is reliably diverted without stopping the line. Employ light curtains or sensors to detect jam conditions and trigger safe shutdowns. Document the integration mapping between multihead weigher discharge cycles and the G5020's trigger output.
Calibration and sensitivity testing — practical steps for reproducible results
Calibration creates a baseline and sets alarm thresholds. Use manufacturer‑recommended calibration routines and authorized test tools. For food industry use, keep certified test pieces (ferrous, non‑ferrous, stainless) in a tamper‑proof kit. Conduct sensitivity tests at the start of each production shift and whenever product, packaging, or line speed changes.
Suggested routine: (1) Warm up the detector per manufacturer instructions. (2) Run empty aperture and recorded product effect checks. (3) Pass the appropriate test pieces at representative positions within the aperture (left/center/right) and record detection readouts. (4) Log results in a calibration register. These steps help maintain traceability for audits (HACCP, BRCGS, FSMA) and prove due diligence.
Validation and verification — meeting regulatory requirements with a metal detector for food industry
Validation proves the detector performs to specification for the product set; verification ensures ongoing performance. Create a validation protocol specifying product samples, packaging, test piece types and sizes, test frequencies, positions, and pass/fail criteria. Aim to demonstrate consistent detection across: different fill levels, common pack orientations, and typical line speeds. A well‑documented validation supports regulatory inspections and customer audits.
Verification schedule example: daily quick checks, weekly full sensitivity tests, and quarterly revalidation following major equipment or product changes. Maintain records for traceability and corrective actions. Industry guideline resources (Campden BRI, BRCGS) provide templates and recommended practices for validation and verification protocols.
Reject strategies: minimize product loss while ensuring safety
Reject strategy design is a tradeoff between safety and yield. A safe default is to divert any detected metal contaminants, but indiscriminate rejection can waste significant product or cause unnecessary downtime. Use tiered approaches: set alarm thresholds based on product risk and customer requirements, configure automatic rejects for confirmed detections, and route uncertain alarms to a manual inspection station where operators can quickly verify and clear minor anomalies.
For product flows from a multihead weigher, consider short diversion chutes for single‑package rejects and larger diverters for bulk rejects. Record all rejects with time stamps and images (if available) to feed into root cause analysis for process improvements that reduce recurring contamination.
Hygiene and maintenance — essential for a certified metal detector for food industry
Hygienic design reduces contamination risk and simplifies cleaning. The G5020's specialized conveyor belt and easy‑disassembly features support quick washdowns and tool‑less belt removal where necessary. Follow a written cleaning schedule aligned with product allergen and microbiological control plans: daily quick cleans, full cleandowns between product types where required, and periodic deep cleans.
Maintenance actions that preserve sensitivity: keep the aperture and conveyor free of debris, check belt tension and tracking, inspect signal cables and earth connections, and replace worn contact surfaces. Log all maintenance with details of tasks performed and parts replaced to support equipment lifecycle management and audit readiness.
Troubleshooting common issues with metal detector for food industry lines
Common problems include false rejects, missed detections, and fluctuating sensitivity. Typical root causes and remedies:
- False rejects: caused by vibration, unstable product flow, or electrical interference. Remedy: secure conveyors, stabilize product feed, and isolate interference sources.
- Missed detections: often due to incorrect frequency selection or poor aperture presentation. Remedy: re‑profile product effect, run validation test pieces, and try different frequency combinations on the G5020.
- Sensitivity drift: caused by temperature changes, dirty apertures, or worn electronics. Remedy: clean aperture surfaces, stabilize environment where possible, and schedule calibration.
Data logging and traceability — turning detector events into actionable insights
Modern detectors like the G5020 can log events, store recipes, and interface with factory data historians. Capture alarm counts, reject volumes, and calibration logs. Use that data to spot trends — for example, a sudden rise in non‑ferrous detections may point to a failing bearing or process change upstream. Automated reports help continuous improvement and provide audit trails for regulators and customers.
How the G5020 compares: multi-frequency vs single-frequency metal detector performance
Multi‑frequency detectors provide superior adaptability across diverse product types and packaging; single‑frequency units can be sufficient for consistent, homogeneous products but struggle with mixed product lines. The table below summarizes typical detection capability ranges for industrial food detectors. Values are approximate and depend on product presentation, aperture size, and detector design. Source: Campden BRI and manufacturer test data.
| Metal Type | Typical Detection Range (mm spherical) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrous | 1.5–2.5 | Usually the easiest to detect; small ferrous slivers detected reliably on most foods. |
| Non‑ferrous (e.g., aluminium) | 2.0–3.5 | Detection varies with product moisture; multi‑frequency helps. |
| Stainless steel (austenitic) | 2.5–4.0 | Least magnetic; requires lower frequency and careful validation. |
Sources: Campden BRI guidance and typical manufacturer performance sheets. Exact values will vary; always validate in your process environment.
Operational SOP checklist for using a metal detector for food industry inspection
Create straightforward SOPs that operators can follow. A concise checklist example:
- Pre‑shift: power up, warm up, and run manufacturer self‑test.
- Product change: load product recipe, run three verification test pieces across aperture, record results.
- During run: monitor alarm LED counts and rejects per hour; escalate if above normal.
- End of shift: export logs, clean detector, and store test kit.
Brand advantages: Why choose the Food Metal Detector Manufacturer For Reject Defective Products G5020
When selecting a detector for high‑value food production, the G5020 presents several advantages:
- Multi‑frequency detection improves detection of stainless and non‑ferrous metals across wet and dry products.
- Hygienic conveyor and easy disassembly reduce downtime for cleaning and maintenance, aiding compliance with EHEDG and food safety programs.
- Designed to integrate with multihead weighers and automatic reject mechanisms to support continuous, high‑throughput lines.
- Built‑in data logging simplifies traceability, audit readiness, and root cause analysis.
These strengths reduce the total cost of ownership by lowering false rejects, minimizing line stoppages, and simplifying audit preparation.
Case example: reducing false rejects in a mixed‑product snack line
A medium‑sized snack manufacturer saw frequent false rejects after introducing a new seasoning blend (higher oil content). By profiling the new product and switching the detector to a combined lower‑mid frequency on the G5020, then validating with test pieces, the plant reduced false alarms by 70% while preserving detection sensitivity. The result: higher yield and improved confidence during customer audits.
FAQs — common questions about using the G5020 metal detector for food industry applications
Q1: How often should we validate the G5020?
A: Perform a full validation when adding new products, packaging changes, or after major maintenance. For ongoing verification: daily quick checks, weekly sensitivity tests, and quarterly reviews are common best practices.
Q2: Can the G5020 detect stainless steel?
A: Yes — especially when using the multi‑frequency mode and optimizing for lower frequencies. Detection size will be larger than for ferrous metals; verify with representative test pieces.
Q3: How do we balance sensitivity and throughput?
A: Sensitivity decreases as line speed and product turbulence increase. Stabilize product presentation, use appropriate frequency settings, and validate at production speed. If necessary, accept slightly higher detection limits to maintain practical throughput but document the rationale for audits.
Q4: What documentation should we keep for audits?
A: Keep calibration logs, validation and verification reports, daily checklists, maintenance records, and event logs showing detected/rejected items. These demonstrate HACCP control and compliance with customer standards like BRCGS.
Q5: How does the G5020 integrate with a multihead weigher?
A: The G5020 can be positioned after the weigher's discharge to inspect each weighed pack. Configure synchronized outputs to confirm triggers and ensure reject timing matches product positions. Consult your integration plan to minimize misrejects.
Contact and next steps — view the product or speak with an expert
To evaluate the G5020 for your production line or request an on‑site demonstration, contact our sales team or request a specification sheet. Our experts can help with line surveys, validation protocols, and integration with your multihead weigher to ensure reliable rejection of defective products while optimizing throughput. Effective inspection strategies directly impact product safety and brand protection. Discover how G5020 reject systems reduce product recalls by ensuring contaminated products are reliably removed from the production line.
Sources
- Campden BRI — Practical guidance on metal detection and validation in food processing (campdenbri.co.uk).
- BRCGS Global Standard for Food Safety — requirements for control of physical contaminants (brcgs.com).
- EHEDG — Hygienic design principles for food processing equipment (ehedg.org).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) — Food Safety Modernization Act (fsma) and guidance documents (fda.gov).
Contact / View product
Contact our sales team to schedule a demo or request detailed specifications for the Food Metal Detector Manufacturer For Reject Defective Products G5020. Ensure your production line has the right metal detector for food industry needs — safer product, fewer recalls, and better yields.
Top Food Metal Detector Models for Packaging Lines 2025
The B2B Buyer’s Guide to automatic check weigher machine
Top 10 pouch packaging machine Manufacturers and Supplier Brands
Best dry food packaging machine manufacturers and supplier brands

Dropped Metal Detector for Powder Granules For Food Industry
Enhance food safety with Kenwei’s Dropped Metal Detector for Powder Granules. This advanced food metal detector ensures precise detection in the food industry, safeguarding products and maintaining high quality standards throughout processing.
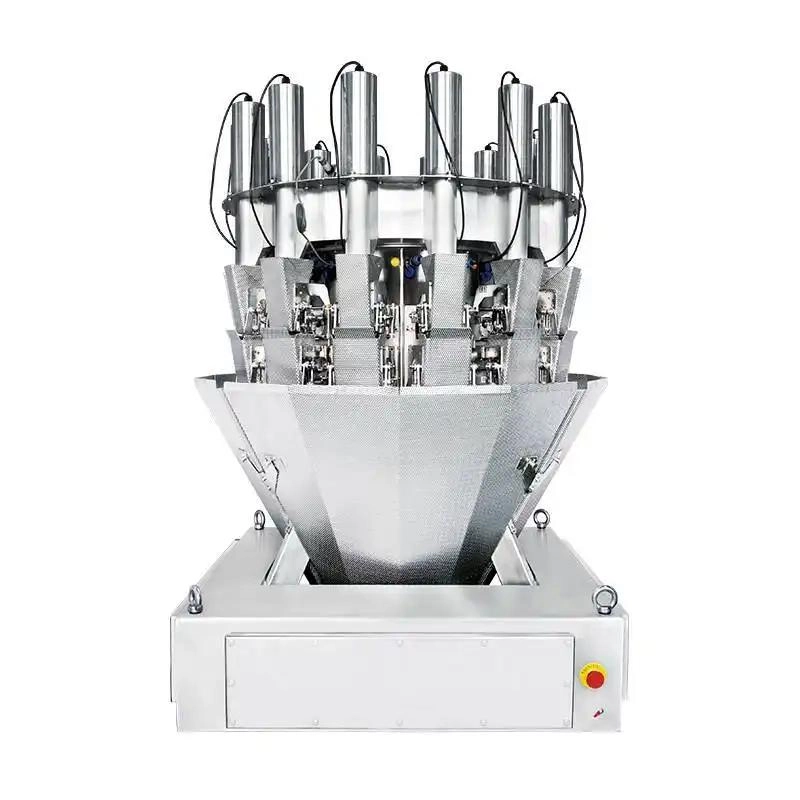

14 Heads Vertical Single Screw Feeding Pickles Weigher backups
This type of weigher is designed to handle the unique characteristics of pickles, ensuring precise measurements for packaging and distribution. It uses a vertical single screw mechanism to feed the pickles into the weighing system, allowing for efficient and consistent weighing. This technology is particularly useful in food processing and packaging facilities where precise portioning is essential for quality control and customer satisfaction. This specialized equipment is perfect for accurately measuring and dispensing pickles in a production line or packaging facility. The vertical design allows for efficient and precise filling of containers, while the single screw feeding mechanism ensures consistent and reliable weighing.

Vertical Frozen Food Packaging Machine for IQF & Frozen Products JW-B1
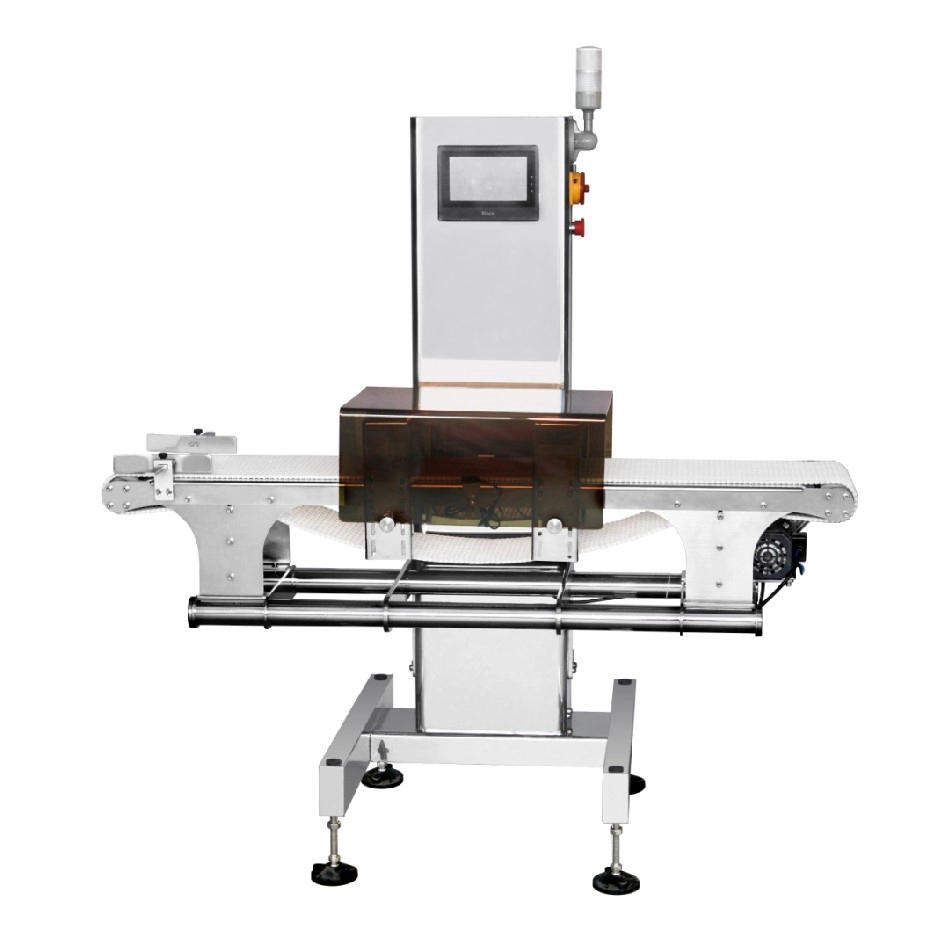

Metal Detector for Aluminum Foil in the Food Industry for Accurate Contamination Detection
The 2415 Metal Detector for Aluminum Foil is equipped with high-sensitivity sensors that effectively filter out signals from aluminum packaging, ensuring precise detection of magnetic metal contaminants. Ideal for detecting foreign bodies in aluminum foil-packaged items such as coffee bags, peanuts, dried meats, chocolate, and more. This versatile metal detector offers adjustable settings, with a maximum width of 24mm and height ranging from 20-150mm, making it suitable for a wide variety of aluminum foil packaging applications.







Kenwei
Kenwei
Kenwei multi weigh
Kenwei
Kenwei
Kenwei